Smart Irrigation Technology
What are the 2 different smart irrigation systems
There are several types of smart irrigation systems that use different technologies and methods to optimize irrigation and water use. Some common types of smart irrigation systems include:
-
Weather-based systems: These systems use data on local weather conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and precipitation, to determine the watering needs of plants. They can be programmed to adjust irrigation schedules based on the weather forecast, helping to reduce water waste and optimize plant health.
-
Soil moisture-based systems: These systems use sensors or probes to measure soil moisture levels and determine the watering needs of plants. They can be programmed to adjust irrigation schedules based on the moisture content of the soil, helping to optimize water usage and plant health.
Both weather-based and soil moisture-based systems can save up to 40% in water consumption compared to traditional irrigation methods, and can also help to improve plant health and reduce the costs associated with treating phytosanitary problems.
Technology based on atmospheric moisture weather conditions.

Weather-based irrigation systems use technology to monitor atmospheric moisture and weather conditions in order to optimize irrigation schedules.These systems can either use a mini field weather station or a weather sensor to collect data on temperature, precipitation, and solar radiation. Alternatively, the system can receive weather data from a meteorological weather forecasting service, which can provide real-time or forecasted data on weather conditions in the area.
The data collected by the weather station or sensor is then used to adjust the watering schedules of the irrigation system. For example, if the weather forecast predicts a period of dry, hot weather, the system may increase the frequency or duration of watering to ensure that plants receive sufficient moisture. On the other hand, if the forecast predicts wet weather, the system may reduce watering or even turn it off completely to avoid over-watering.
Overall, weather-based irrigation systems can help to optimize water usage and reduce waste by adjusting watering schedules based on real-time or forecasted weather conditions.

Technology based on atmospheric moisture weather conditions.
Weather-based irrigation systems use technology to monitor atmospheric moisture and weather conditions in order to optimize irrigation schedules.These systems can either use a mini field weather station or a weather sensor to collect data on temperature, precipitation, and solar radiation. Alternatively, the system can receive weather data from a meteorological weather forecasting service, which can provide real-time or forecasted data on weather conditions in the area.
The data collected by the weather station or sensor is then used to adjust the watering schedules of the irrigation system. For example, if the weather forecast predicts a period of dry, hot weather, the system may increase the frequency or duration of watering to ensure that plants receive sufficient moisture. On the other hand, if the forecast predicts wet weather, the system may reduce watering or even turn it off completely to avoid over-watering.
Overall, weather-based irrigation systems can help to optimize water usage and reduce waste by adjusting watering schedules based on real-time or forecasted weather conditions.

These systems can be particularly useful in areas with variable weather conditions, as they can help to ensure that plants receive the right amount of water at the right times, regardless of changes in the weather.
The data collected by the weather sensors or weather forecasting service is used to adjust the watering times or schedules based on the specific needs of the soil and irrigation method being used. This can help to optimize water usage and improve plant health, leading to better crop yields and reduced water bills.
Weather-based irrigation systems use data on temperature, wind, solar radiation, and humidity to optimize watering schedules and ensure that plants receive the right amount of water at the right times.
These systems can be particularly useful in areas with variable weather conditions, as they can help to ensure that plants receive the right amount of water at the right times, regardless of changes in the weather.
The data collected by the weather sensors or weather forecasting service is used to adjust the watering times or schedules based on the specific needs of the soil and irrigation method being used. This can help to optimize water usage and improve plant health, leading to better crop yields and reduced water bills.

Soil moisture based technology
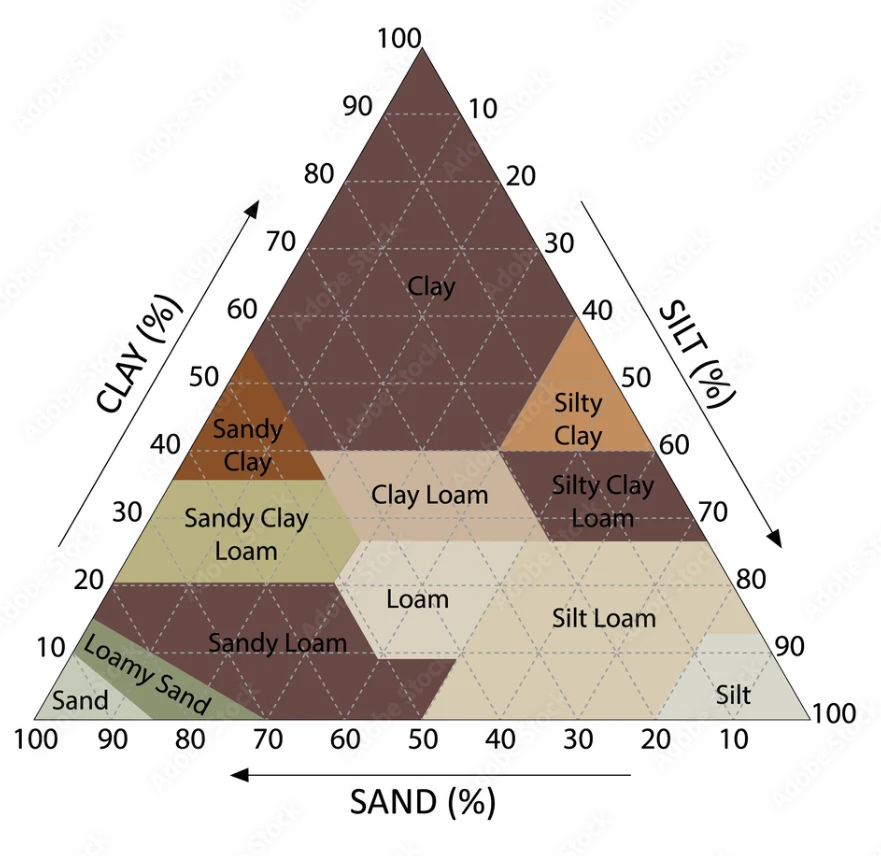
These systems provide information on the soil water capacity at the active depth of the plant''s root system, which can be used to optimize watering schedules and reduce water waste.
The water capacity of soil refers to the amount of water that the soil can hold after it has been drained, and it is an important factor in determining the watering needs of plants. Water capacity can vary significantly depending on the type of soil, with sandy soils typically having a lower water capacity (around 7%) compared to clay soils (around 40%).
By continuously monitoring soil moisture levels, soil moisture-based irrigation systems can help to ensure that plants receive the right amount of water at the right times, improving plant health and reducing the risk of overwatering or underwatering.

Soil moisture based technology
Soil moisture-based irrigation systems use sensors to measure the moisture content of the soil and adjust watering schedules accordingly.
These systems provide information on the soil water capacity at the active depth of the plant''s root system, which can be used to optimize watering schedules and reduce water waste.
The water capacity of soil refers to the amount of water that the soil can hold after it has been drained, and it is an important factor in determining the watering needs of plants. Water capacity can vary significantly depending on the type of soil, with sandy soils typically having a lower water capacity (around 7%) compared to clay soils (around 40%).
By continuously monitoring soil moisture levels, soil moisture-based irrigation systems can help to ensure that plants receive the right amount of water at the right times, improving plant health and reducing the risk of overwatering or underwatering.
Ardefsis Technology utilizes both of these technologies in combination for better results.
The Ardefsis smart irrigation and watering system combines weather and soil moisture technologies to provide a more comprehensive and accurate view of watering needs, leading to better results.
It is designed to be compatible with any existing irrigation system, requiring no changes to the existing infrastructure. As long as there is an electric valve present in each watering zone, the system can be easily integrated and begin regulating the supply of water to each solenoid valve based on the specific watering needs of each zone.
The central controller then opens and closes the supply to each solenoid valve as needed, helping to optimize water usage and improve crop health and production. Overall, the Ardefsis system provides an effective and efficient solution for optimizing irrigation and watering practices.